Do organisations have electrostatic control practices and are there any reasons to be concerned? These questions are important in light of successive advances in medical device technology, combined with hardware developments, mean static discharge and electrostatic discharge (ESD) could be critical for patient and equipment safety in hospitals.
As ESD thresholds increase in production areas (technical, scientific or medical operations sectors using cleanroom operation areas), the awareness and control methodologies become a threat: damage from ESD is often difficult to detect until failure.
Many electronic components, especially microchips and semiconductors, can be damaged by ESD forces. Sensitive components need to be protected during and after manufacture, during shipping, device assembly, and in the finished item. Grounding is especially important for effective ESD control. It should be clearly defined and regularly evaluated.
Static build-up
Many of the frequently used insulating materials in cleanrooms, such as plate glass, Teflon and polymers, are construction items that can become highly charged during normal everyday operations.
Individual workstations are a potential concern for static build-up, as is the use of stainless steel work surfaces compared with static dissipative work surfaces. Conductive work surfaces can also be considered a current-carrying hazard to both people and ESD-sensitive devices.
Besides static electricity, the issue around electrostatic attraction (ESA) is also important to control. Avoiding ESA improves the general cleanliness in a healthcare environment by reducing the risk of hospital infections carried by airborne contaminants, which may otherwise be attracted to the charged surfaces.
ESD control considerations
The measures for ESD control in a cleanroom are a representative selection of the following products and materials:
- ESD flooring
- Static control workstations
- Conveyors, racks & storage
- Plexiglas or polycarbonate enclosures
- Stationery, paper & consumables
- Transfer carts or trolleys
- ESD safe chairs
- Garments, facemasks, snoods, gloves, shoes & overshoes etc
- Ionization equipment
- ESD monitoring & testing equipment
- ESD materials, static shielding bags, Jedec trays
Medical instruments and specifically data processing equipment can be susceptible to ESD, especially when electromagnetic compatibility does not cover the complete system of instrumentation.
ESD immunity testing based on a human metal connection ensures safety, but all the possible combinations of instruments with data processing and audio-visual systems are not necessarily tested.
A key area of danger is static electricity in the presence of flammable gases, liquids and other flammable materials
Disruptions and damages have been reported over recent years, but in most cases, root causes of the ESD failures cannot be traced. ESD malfunctions and damages are generally classified as unknown electric failures.
A key area of possible danger is static electricity in the presence of flammable gases, liquids and other materials that could be incendiary.
The use of flammable substances in healthcare facilities has decreased, but without the control, the risk of fires and explosions can still occur, especially in laboratories, intensive care units, and operating rooms.
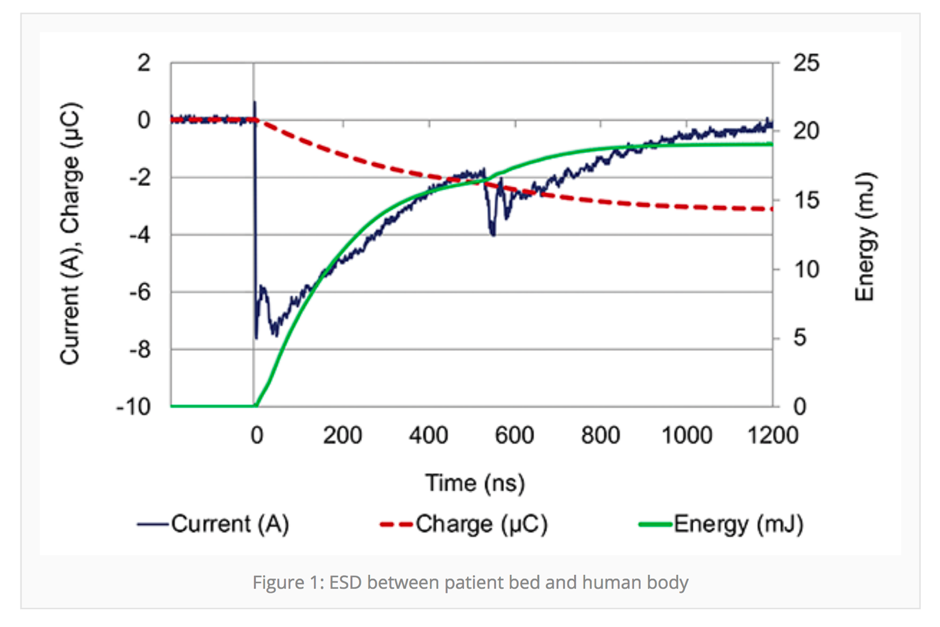
Electrostatic shock to people is also a real and ever-present risk. ESD energy can be high enough to cause painful sensations to patients and healthcare personnel, resulting in involuntary movements, which can lead to accidents. Figure 1 below shows an electrostatic discharge captured from the patient bed. In this example, the electric potential of the bed was 14,000v and the discharge energy integrated over 1500Ω human body resistance was approximately 20mj.
Electrostatic control considerations in controlled environments and specifically healthcare, vary greatly on the medical procedures, locations and activities. But grounding of personnel and other conductors is required in certain locations, where temporary losses of functions of medical equipment pose a significant risk to the life of patients. A selection of the materials to reduce residual charge levels is recommended in all locations.
Customers who want to equip their cleanrooms with ESD equipment must verify a supplier's claims for both ESD compliance and product cleanliness.

